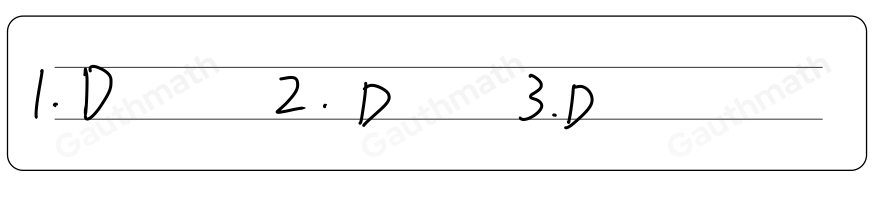
1. What do you call to the selection of objects regardless of their order? A. combination B. differentiation C. integration D. permutation 2. How many ways can a code be formed from the digits 0 to 9 if a combination lock must contain 5 different digits? A. 15120 B. 30240 C. 151200 D. 1000000 3. Which of the following situations does NOT illustrate combination? A. Selecting 2 songs from 10 choices for an audition piece. B. Fixing the schedule of a group of students who must take exactly 8 subjects. C. Enumerating the subsets of a set D. Identifying the lines formed by connecting some given points on a plane. 1 Math 10 Qtr 3 Module 3
Question